News
Radon
Radon
Radon is a colourless, odourless radioactive gas. It is formed by the radioactive decay of the small amounts of uranium that occur naturally in all rocks and soils.
Radioactive elements decay and emit radiation. Any exposure to this type of radiation is a risk to health – radiation is a form of energy and can cause damage in living tissues increasing the risk of cancer.
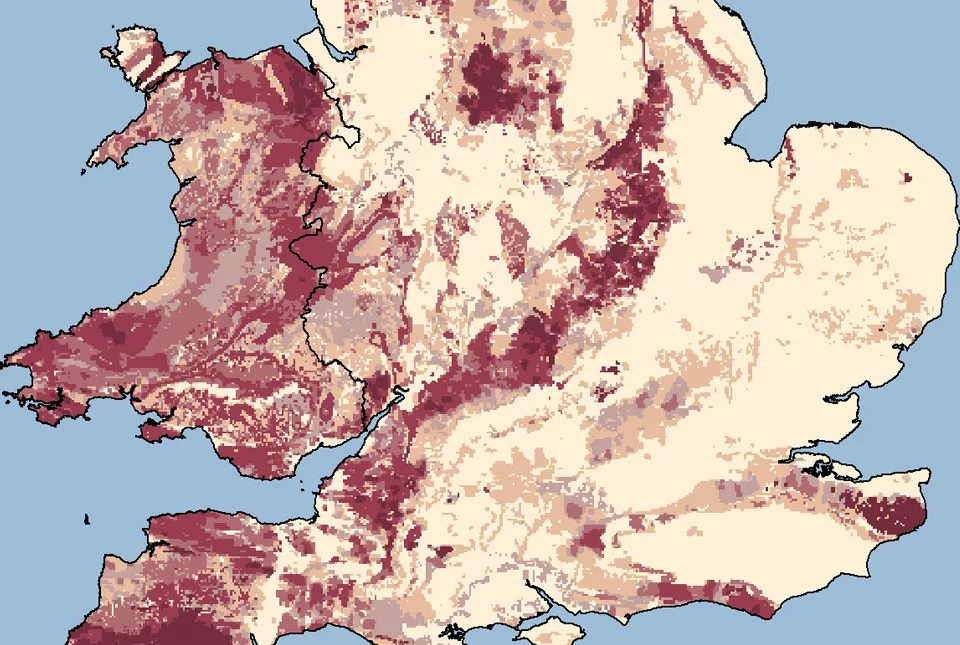
Radon is everywhere; formed from the uranium in all rocks and soils. Outdoors everywhere and indoors in many areas the radon levels are low and the risk to health is small. The darker the colour on the radon maps, the greater the chance of a high radon level in a building. However not all buildings, even in the darkest areas, have high levels.
The amount of radon is measured in becquerels per cubic metre of air (Bq m-3). The average level in UK homes is 20 Bq m-3. For levels below 100 Bq m-3, your individual risk remains relatively low and not a cause for concern. However, the risk increases as the radon level increases.
Radioactivity is where unstable elements, such as naturally occurring uranium, thorium and radon, break down; energy is released and different elements formed. The new elements may also be unstable so the process is repeated until a stable element is formed. The energy given off is called radiation and can be alpha or beta particles or gamma rays. Alpha particles are more harmful than beta particles or gamma rays. This is because alpha particles contain more energy and are absorbed over a smaller area.
The ground is the main source of radon.
The aim of remedial work is to reduce radon levels as low as possible. There are several methods that can be used to reduce high radon levels.
- Radon sump – An active radon sump, fitted with a fan, is the most effective way to reduce indoor radon levels. Sumps work best under solid floors and under suspended floors if the ground is covered with concrete or a membrane. Occasionally, passive sumps without a fan may reduce radon levels.
- Positive Ventilation – A small quiet fan blows fresh air, usually from the roof space, into the building. PIV units for both flats and loft spaces are available.
- Natural under-floor ventilation – Many homes and some workplaces have a suspended ground floor with a space underneath. Good ventilation of this space can reduce radon concentrations. Airbricks provide a natural way of introducing fresh air.
- Active under-floor ventilation – A fan is used to either continuously blow air into or extract air out from the space below a suspended floor. This can be used when natural under-floor ventilation is inadequate to reduce radon level. Our WMF fan is an ideal unit to help with removing Radon.